EnumGithub REST API for Gistsnonnull and required=Truexxx_id and xxx
is an existing modelselect_related at first resolver to speed up
further model property access based on GraphQL query to reduce total
amount of sql call and thus improve performancevalidate_state_code=True by defaultxx_deleted
insteadwith transcation.atomic()
with transcation.atomic()submit_entity_unhandled@transaction.atomic to avoid future
changes that introduces errors in error handling logicsget_or_create?Error Handling means what are the correct business
logics when errors happenwith transaction.atomic():
task = Task.objects.create(...) # or update some properties then task.save()
submit_entity_unhandled()# if response data is needed
foo_id = third party POST or PATCH
save `foo_id` to local DB# if response data is not needed
with transaction.atomic():
local db changes()
third party POST or PATCHAnswer:
Method: POST
PATH: /gists
JSON Data:
{"description":"Example of a gist","public":false,"files":{"sample.md":{"content":"Hello World"}}}
Response Status Code On Success: 201
Example Response:
{
"url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2",
"forks_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2/forks",
"commits_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2/commits",
"id": "2decf6c462d9b4418f2",
...Curl
curl -L \
-X POST \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR-TOKEN>" \
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
https://api.github.com/gists \
-d '{"description":"Example of a gist","public":false,"files":{"sample.md":{"content":"Hello World"}}}'Method: GET
PATH: /gists/{gist_id}
Response Status Code On Success: 200
Example Response:
{
"url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2",
"forks_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2/forks",
"commits_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2/commits",
"id": "2decf6c462d9b4418f2",
...Response Status Code On Resouce Not Found: 404
Curl
curl -L \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
https://api.github.com/gists/GIST_IDMethod: PATCH
PATH: /gists/{gist_id}
Response Status Code On Success: 200
Example Response:
{
"url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2",
"forks_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2/forks",
"commits_url": "https://api.github.com/gists/2decf6c462d9b4418f2/commits",
"id": "2decf6c462d9b4418f2",
...Response Status Code On Resouce Not Found: 404
Curl
curl -L \
-X PATCH \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR-TOKEN>" \
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
https://api.github.com/gists/GIST_ID \
-d '{"description":"An updated gist description","files":{"sample.md":{"content":"Hello World from GitHub"}}}'Method: DELETE
PATH: /gists/{gist_id}
Response Status Code On Success: 200
Example Response: No return Data
Response Status Code On Resouce Not Found: 404
Curl
curl -L \
-X DELETE \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR-TOKEN>" \
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
https://api.github.com/gists/GIST_IDScrupulous writers, in every sentence that they write, will ask themselves at least four questions:
Two more that they may ask are:
Consequently there are ways to write well. The following rules will cover most cases:
doc string if there is anything unclearfish
instead bashParallelism
single-threaded program can only use one CPU core where a multi-threaded program can use multiple CPU Cores.
Avoid blocking slow I/O
Some threads waits for slow blocking I/O, while other threads can perform useful computation.
Threading enables overlap of I/O with other activities within a single program, much like multiprogramming did for processes across programs.
Many morden server-based application such as web servers, database management systems, make use of threads in their implementations
One could still use multi-process instead of multi-thread, but threads share memory (an address space) thus make it easy to share data. multi-processes are better choice for logically separate tasks where little shareing of data structures in memory is needed.
hexadecimal dump of ascii charaters
Control characters may be described as doing something when the user inputs them, such as code 3 (End-of-Text character, ETX, ^C) to interrupt the running process, or code 4 (End-of-Transmission character, EOT, ^D), used to end text input on Unix or to exit a Unix shell. These uses usually have little to do with their use when they are in text being output.
The control characters in ASCII still in common use include:
hex: 00 (decimal: 00, null, NUL, \0, ^@), originally
intended to be an ignored character, but now used by many programming
languages including C to mark the end of a string.hex: 07 (decimal: 07, bell, BEL, \a, ^G), which may
cause the device to emit a warning such as a bell or beep sound or the
screen flashing.hex: 08 (decimal: 08, backspace, BS, \b, ^H), may
overprint the previous character.hex: 09 (decimal: 09, horizontal tab, HT, \t, ^I),
moves the printing position right to the next tab stop.hex: 0A (decimal: 10, line feed, LF, \n, ^J), moves the
print head down one line, or to the left edge and down. Used as the end
of line marker in most UNIX systems and variants.hex: 0B (decimal: 11, vertical tab, VT, \v, ^K),
vertical tabulation.hex: 0C (decimal: 12 form feed, FF, \f, ^L), to cause a
printer to eject paper to the top of the next page, or a video terminal
to clear the screen.hex: 0D (decimal: 13, carriage return, CR, \r, ^M),
moves the printing position to the start of the line, allowing
overprinting. Used as the end of line marker in Classic Mac OS, OS-9,
FLEX (and variants). A CR+LF pair is used by CP/M-80 and its derivatives
including DOS and Windows, and by Application Layer protocols such as
FTP, SMTP, and HTTP.hex: 1A (decimal: 26, Control-Z, SUB, ^Z), Acts as an
end-of-file for the Windows text-mode file i/o.hex: 1B (decimal: 27, escape, ESC, \e (GCC only), ^[).
Introduces an escape sequence.from man ascii
od
to see the hex value for charactersod -t a -t x1 -t c
-t a - prints in ascii format-t x1 - prints in hex format-t c - prints in c escape formate.g.
> printf '\0\a\b\n\r\t\v ' | od -t a -t x1 -t c
0000000 nul bel bs nl cr ht vt sp
00 07 08 0a 0d 09 0b 20
\0 \a \b \n \r \t \v
0000010https://www.soscisurvey.de/tools/view-chars.php
\033[XXXm is Select Graphic Rendition subset of ANSI
escape sequences, \033 is actually ESC character in ascii
octal format, \e is equivalent in zsh shell, however, don’t
use \e, \e is not recognised in
awk nor python.
> echo "\033[31mRed Text\033[0m"
Red Text
> echo "\e[31mRed Text\e[0m"
Red Text\033[ - Begin the color modificationsCODEm - CODE + m at the end\e[0m - End the color modifications| code | description |
|---|---|
30, 90 |
fg black |
31, 91 |
fg red |
32, 92 |
fg green |
33, 93 |
fg brown |
34, 94 |
fg blue |
35, 95 |
fg purple |
36, 96 |
fg cyan |
37, 96 |
fg light grey |
40 |
bg black |
41 |
bg red |
42 |
bg green |
43 |
bg brown |
44 |
bg blue |
45 |
bg purple |
46 |
bg cyan |
47 |
bg light grey |
0 |
reset / normal |
1 |
bold |
3 |
italic |
4 |
underline |
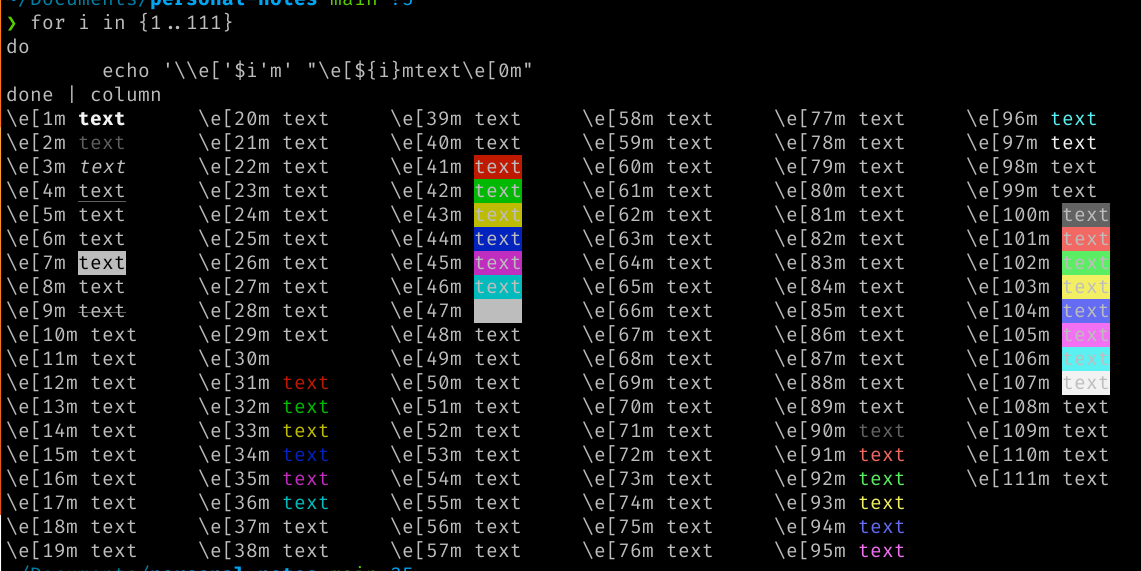
> for i in {1..111}
do
echo '\\e['$i'm' "\e[${i}mtext\e[0m"
done | column
See also: a comprehensive explanation
Authentication is the process of verifying that “you are who you say you are”
Authorization is the process of verifying that “you are permitted to do what you are trying to do”
A key feature of true event-driven architectures is that the producers and consumers are completely decoupled – a producer shouldn’t know or care who is consuming its events and how the consumers use those events in their service..
Examples
Two key characteristics of event-based compute
Examples
See also origin of this idea
SaaS is a business and software delivery model that gives organisations the ability to offer their solutions in a low-friction, service-centric model that maximises value for customers and providers. It relies on agility and operational efficiency as pillars of a business strategy that promotes growth, reach and innovations.
Typically,
Importantly, if some text is encrypted with private key, only public key can decrypted it.
If some text is encrypted with public key, only private key can decrypted it.
For example, HTTPS handshake is basically, I get the Public Key of a website, generate a random password, encrypt it with Public Key and then send it to the website server and then website server uses Private Key to decrypt the password, so this password is shared. And further communication is encrypted using that shared password.
But really, public key isn’t just for encryption nor private for decryption, the otherway around works too, private key can be used for encryption and public key for decryption.
One example that uses private key for encryption is digital signature, take some text/file, create a digest of test/file, encrypt the digest with private key and send the encrypted digest together with the text/file. Then if the public key successfully decrypt the encrypted digest and the digest matches then we know the test/file is the original, because the only key that can encrypt something that can be decrypt with public key is the private key.
The only reason public and private keys are not interchangeable is because you can recreate the public key from private key.